

Set to 1 if a solution was found, otherwise refer Upper triangular matrix produced by QR factorizationĪn integer flag. The orthogonal matrix, q, produced by the QRįactorization of the final approximate Jacobian The solution (or the result of the last iteration forĪ dictionary of optional outputs with the keys: nfev N positive entries that serve as a scale factors for the factor float, optionalĪ parameter determining the initial step bound That the relative errors in the functions are of the order of IfĮpsfcn is less than the machine precision, it is assumed epsfcn float, optionalĪ suitable step length for the forward-differenceĪpproximation of the Jacobian (for fprime=None). Jacobi matrix is considered banded (only for fprime=None). fsolve implements three different algorithms: trust region dogleg, trust region reflective. Super-diagonals within the band of the Jacobi matrix, the fsolve solves systems of nonlinear equations of several variables. If set to a two-sequence containing the number of sub- and 2 Answers Sorted by: 0 Prove that there is only one root, so you don't need to search further. If zero, thenġ00*(N+1) is the maximum where N is the number of elements The maximum number of calls to the function. The calculation will terminate if the relative error between twoĬonsecutive iterates is at most xtol. The columns (faster, because there is no transpose operation). Specify whether the Jacobian function computes derivatives down By default, the Jacobian will be estimated.

fprime callable f(x, *args), optionalĪ function to compute the Jacobian of func with derivativesĪcross the rows. args tuple, optionalĪny extra arguments to func. The starting estimate for the roots of func(x) = 0. So, I am trying to use fsolve and i follow the example given on documentation of fsolve. I never use matlab before but i am trying to learn for my project. Parameters : func callable f(x, *args)Ī function that takes at least one (possibly vector) argument,Īnd returns a value of the same length. 1 I want to develop a desktop application for solving system of linear and nonlinear equations. Return the roots of the (non-linear) equations defined byįunc(x) = 0 given a starting estimate. fsolve ( func, x0, args = (), fprime = None, full_output = 0, col_deriv = 0, xtol = 1.49012e-08, maxfev = 0, band = None, epsfcn = None, factor = 100, diag = None ) # All the tutorials are completely # scipy.optimize.
#F solve matlab free
This website contains more than 200 free tutorials! Every tutorial is accompanied by a YouTube video.
#F solve matlab code
The code lines 9-10 are used to verify the solution. Finally, on the code line 7, we solve the system.
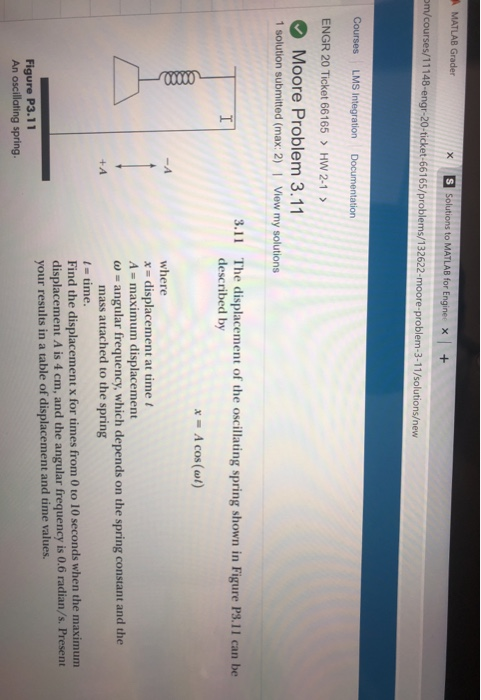
Since MATLAB solves the nonlinear system using iterative methods, we need to initialize the solver with an initial_guess. On the code line 4, we choose an initial condition.

Finally, with the option ‘OptimalityTolerance’ -> 1.0000e-8, we set the solution tolerance. Since we want to speed up the computations, we set ‘UseParallel’ -> true (although for a small system that we are dealing with, the parallel option does not lead to any significant increase in the computation speed). We set the ‘Display’ option to ‘iter’ since we want to monitor and display the solver progress. We use the “trust-region-dogleg” algorithm. On the code line 3 we set the solver options. We use the MATLAB function fsolve() to solve the nonlinear system of equations. solve Equations and systems solver collapse all in page Support for character vector or string inputs has been removed. % Possible algorithms 'trust-region-dogleg', 'trust-region', or 'levenberg-marquardt'


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
